Carbon Ring With One Double Bond
Also what would the molecular formula be.

Carbon ring with one double bond. Cyclohexene is an alicyclic compound with a double bond. Original poster 1 point 6 years ago. An sp 2 hybridized orbital and a p orbital that is not involved in the hybridization form a double bond while a triple bond evolves from an sp hybridized orbital and two p orbitals from each atom. Where would the double bond appear and why.
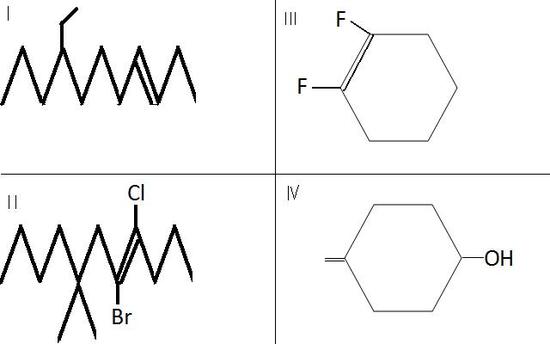
It is actually 1 methylcyclohexene. Otto wallach a german chemist received the 1910 nobel prize in chemistry for his work on alicyclic compounds. L l l. Each carbon of the double bond uses its three sp 2 hybrid orbitals to form sigma bonds to three atoms the other carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
Hope this helps you out ps sorry for my bad english. 2 methylcyclohexene does not exist. 2 methylcyclohexene indicates that the methyl group is bonded to one side of a carbon carbon double bond in a six carbon ring. A double bond is formed with an sp 2 hybridized orbital and a p orbital that is not involved in the hybridization.
The ring is not a flat hexagon but puckered with slightly different side lengths and angles 1200 from the regular hexagon. The formula would be something. A triple bond is formed with an sp hybridized orbital and two p orbitals from each atom. Can we just say that the triply bonded ccc is linear so in a six membered carbon ring in order to be completely.
This bond lies outside the main cc axis with half of the bond on one side of the molecule. The molecule consists of a six membered ring with five oxygen and one carbon atom and one oxygen with a double bond with the carbon. The use of the p orbitals forms a pi p bond. For example all of the bonds in a are exactly the same length due to symmetry whereas the triple bonds in b will be shorter than the adjacent single bonds.
Understanding the hybridization of its orbitals is essential. H h h h h. Hmm this is harder to visualize than the above explanation. Carbon atoms form double bonds in compounds called alkenes and triple bonds in alkynes.
The nomenclature used for the various monocyclic nitrogen containing six membered ring compounds is given below. Carbon is one. L l l l l. Therefore a c are isomers.
The pyridones are aromatic compounds because of contributions to. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds in compounds called alkenes or triple bonds in compounds called alkynes. Spiro compounds have two or more rings that are connected through only one carbon atom. Heterocyclic compound heterocyclic compound six membered rings with one heteroatom.
Going around the ring starting at the carbon to oxygen bond the. The mode of ring closing in the formation of many alicyclic compounds can be predicted by baldwins rules. The use of the p orbitals forms a pi bond. While all of the carbons in these molecules are more or less cesp hybridized the molecules are different from one another due to differences in bond lengths and bond angles.
Positions on the ring are shown for pyridine arabic numerals being preferred to greek letters although both systems are used. Therefore mostly double bonds will occur in six membered carbon rings because it makes the ring way more stable. The molecule that has been observed has a c s symmetry.